3. Testing
3.1. Create a User in Cognito
We should now have a fully working API. Let's test it, but for that we need a user to authenticate with.
To do so, connect to the AWS console, and go to Amazon Cognito.
Open the Cognito user pool name AWS AppSync Workshop User Pool and go to App Integrations. Under App clients and analytics, copy the clientId of the AWS AppSync Workshop Client.
Then execute this command, replace the following values:
clientIdThe client id you copied in Amazon CognitousernamePick a name for your userpasswordPick a password. Passwords must contain at least 8 characters, have at least one number, one lowercase character, one uppercase character and one special character.emailthe email address of your user. The email must be real and valid. You will need to validate it in the following step.
aws cognito-idp sign-up --client-id "{clientId}" --username "{username}" --password "{password}" --user-attributes Name=email,Value="{email}"
example
aws cognito-idp sign-up --client-id "3un93evcbfcc87jdp6jfc94ig0" --username "ben" --password "AppSync101!" --user-attributes Name=email,Value="ben@example.com"
{
"UserConfirmed": false,
"CodeDeliveryDetails": {
"Destination": "b***@g***",
"DeliveryMedium": "EMAIL",
"AttributeName": "email"
},
"UserSub": "de42fece-e9c5-4c89-933e-7647ef8aa1f9"
}
You should immediately receive an email with a verification code. Copy the code and execute the following command. Again, replace the appropriate values.
aws cognito-idp confirm-sign-up --client-id "{clientId}" --username "{username}" --confirmation-code {verificationCode}
If the command does not return any error, it means it worked as expected.
3.2. Test Queries and Mutations
Now that you have a user, it's time to try a few Queries and Mutations. For that, you can use the GraphQL client of your choice (e.g. Postman), but I invite you to use GraphBolt. GraphBolt is a desktop app that helps developers build, test and debug AWS AppSync APIs. It comes with a GraphQL client that is specially tailored for AWS AppSync.
If you prefer, you can also use the AWS AppSync console. Open the created API and go to the Queries tab.
Since we are starting from scratch, we don't have any data in our Database. Let's start by creating a Project first.
Login with your username and password. if you are using GraphBolt, you can do so by clicking on the padlock icon on the top right (see documentation). From the AWS AppSync console, click on Login with User Pool. In both cases, you will need to select the user pool, client and enter your username and password.
Execute the following request.
mutation CreateProject {
createProject(input: { name: "Project1", description: "My first Project" }) {
id
name
description
createdAt
updatedAt
}
}
If everything went well, you should see a result like this one:
{
"data": {
"createProject": {
"id": "1d49e592-e489-43cc-8ce5-d7d99a731cc4",
"name": "Project1",
"description": "My first Project",
"createdAt": "2024-01-11T17:29:57.809Z",
"updatedAt": "2024-01-11T17:29:57.809Z"
}
}
}
Now, go to DynamoDB, and open the Projects table. (its name should be appsync-typescript-workshop-dev-projects). You should see that the item was persisted.
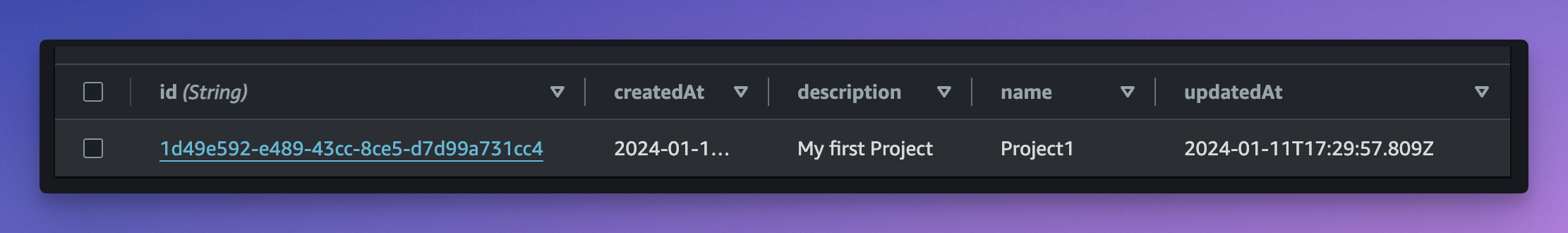
Do the same, and create a new Task. Don't forget to replace projectId with the id of the project that was previously created. Also replace ben with your own username in assignees.
mutation CreateTask {
createTask(
input: {
title: "Task 1"
description: "My first task"
priority: 10
status: TODO
projectId: "1d49e592-e489-43cc-8ce5-d7d99a731cc4"
assignees: ["ben"]
}
) {
id
title
description
priority
status
createdAt
updatedAt
assignees
}
}
{
"data": {
"createTask": {
"id": "ef01da5e-79fd-4e56-97f0-e755f7b82d8c",
"title": "Task 1",
"description": "My first task",
"priority": 10,
"status": "TODO",
"createdAt": "2024-01-11T17:34:51.546Z",
"updatedAt": "2024-01-11T17:34:51.546Z",
"assignees": ["ben"]
}
}
}
Great. I'll let you play with other requests. Try to create a few more tasks and projects, then use the Query.listTasks to get all the tasks from a project. Also try to update and delete tasks using the updateTask and deleteTask mutations.